Defect Detection from SEM/AFM Images
AI-powered microscopy image analysis that auto-analyzes 90% of SEM and AFM images with 95% defect detection accuracy, reducing processing time by 85%.
Challenge
Quality teams review thousands of SEM and AFM images per lot to find and classify manufacturing defects. Analysts jump between image repositories, LIMS, PLM, defect databases, spreadsheets, and report templates. Each batch takes 2–3 days and outcomes vary by technician, limiting trend analysis and slowing release.
The objective: auto-analyze ≥90% of microscopy images with 95% defect detection accuracy and reduce processing time by 85%.
Solution: How AIP changed the operating model
Learning and setup
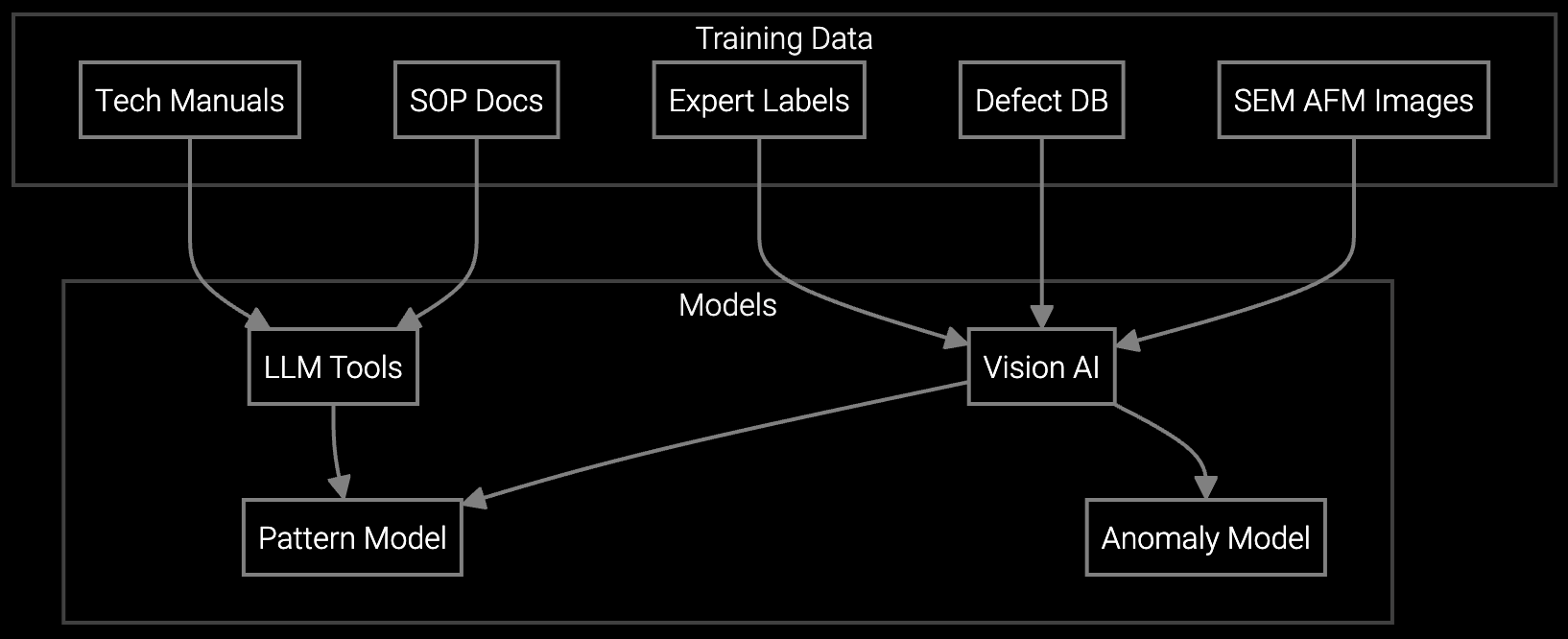
Powered by the Aftermarket Intelligence Platform (AIP), the agentic solution applied vision, pattern, anomaly, computer vision, and LLM integration models. Training data came from historical microscopy images, annotated defect databases, technical manuals, SOP documents, and expert labeled patterns. This enabled the AI agent to recognize and interpret SEM and AFM images, batch identifiers, equipment parameters, defect types, and surface characteristics.
Workflow orchestration
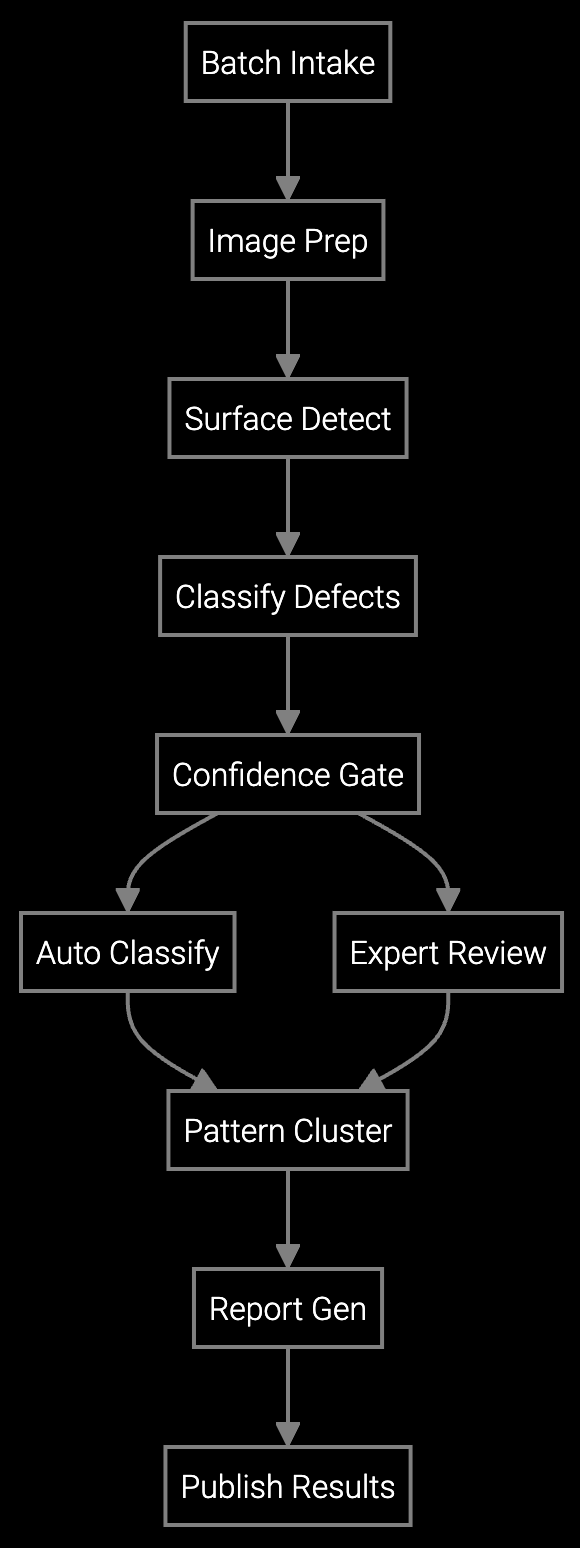
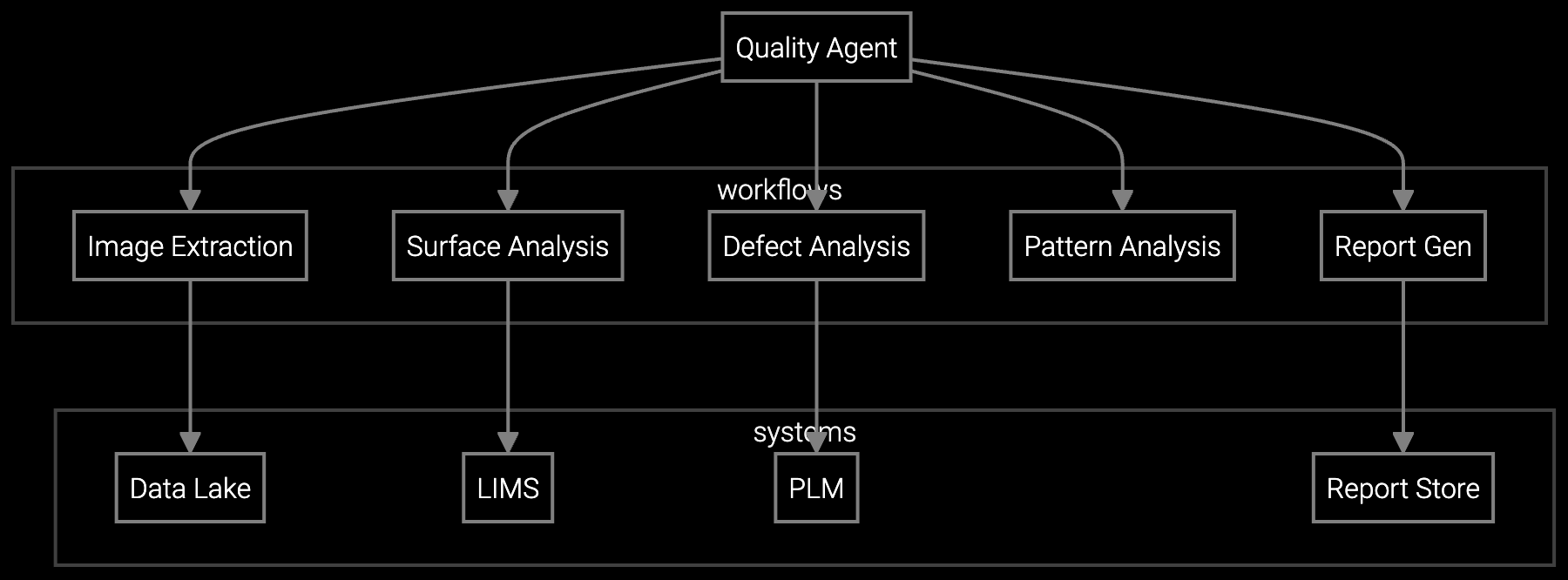
The AI agent analyzes incoming lots, extracts batch identifiers, and routes work across five parallel workflows: image extraction, surface analysis, defect analysis, pattern analysis, and report generation. It navigates data lake, LIMS, PLM, and report stores, mirroring the sequence QA teams follow. Orchestration logic branches when rules apply; for example, low contrast images or conflicting features trigger expert review, while high confidence detections flow to auto classification with policy checks.
Execution and resolution
The AI agent executes each step: extracts images from Excel and PDF sources, aligns and preprocesses frames, detects surface lines and scratches, classifies defects into seven categories, clusters patterns across samples, and generates standardized quality reports. Responses are completed in hours, with updates posted to LIMS and PLM. Exceptions such as unreadable files, novel defect signatures, or missing metadata are routed to engineers with full context and annotated visuals.