When fab equipment downtime costs exceed $1M per hour, technicians can't afford to waste minutes searching for parts or procedures.
Semiconductor field service automation eliminates manual job planning by auto-staging parts, pre-loading tool history, and generating step-by-step repair procedures from telemetry—transforming technicians from searchers into executors who validate AI-prepared service plans.
Technicians spend 45+ minutes before each service call cross-checking tool history, PM schedules, consumables usage, and recipe changes across disconnected systems. For lithography tools with 200+ chamber components, identifying the right parts becomes guesswork.
Without predictive staging, 30% of dispatch calls result in missing parts at the fab. Technicians order replacements on-site, extending tool downtime by 4-8 hours while waiting for expedited chamber kits or consumables—multiplying fab losses exponentially.
After completing repairs, technicians manually enter parts consumed, actions taken, and findings into FSM systems—adding 30-40 minutes per job. For high-volume service teams managing 8-12 daily calls, this administrative load costs 4-5 hours of productive time daily.
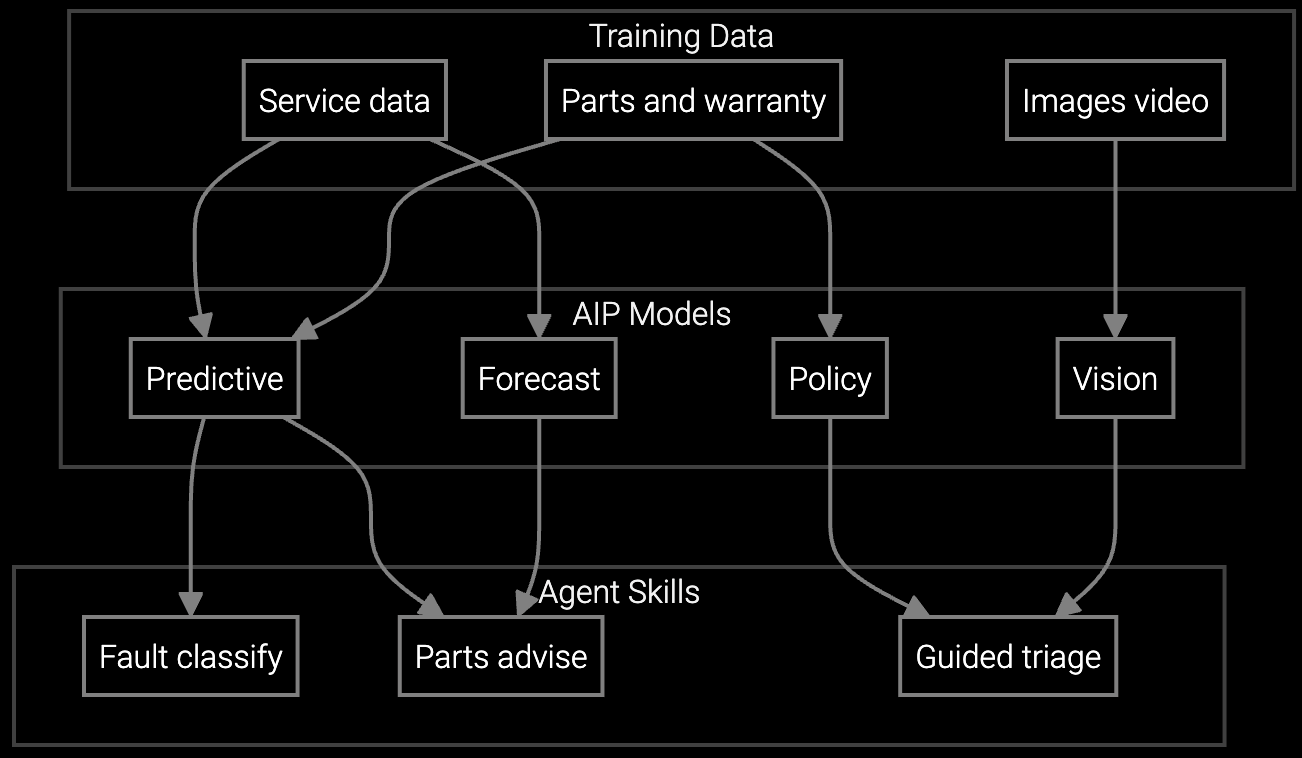
The platform ingests tool telemetry, PM logs, parts consumption history, and failure patterns to auto-generate complete service plans before dispatch. When a work order triggers, AI predicts required parts with 92% accuracy, pre-loads tool configuration history, and assembles step-by-step procedures—delivering a ready-to-execute job package to the technician's mobile device.
On-site, technicians validate AI recommendations rather than researching from scratch. Post-repair, the platform auto-populates FSM fields using photos of replaced parts, telemetry snapshots, and repair notes captured via voice—reducing documentation time from 35 minutes to under 5 minutes. The technician reviews and submits; the system handles data entry.

Predicts which chamber components, consumables, and spares technicians need for lithography and etch tool repairs based on failure codes and PM cycle data.

Correlates tool sensor anomalies with historical failure patterns and process engineer notes to pinpoint root cause of wafer defects or throughput drops.
Mobile copilot delivers repair procedures, diagnostic flowcharts, and replacement instructions for complex tools like EUV scanners directly on the fab floor.
Semiconductor tools operate with nanometer precision and thousands of monitored parameters. A single lithography system generates 50+ telemetry streams tracking vacuum pressure, laser alignment, reticle positioning, and wafer stage accuracy. When OEE drops below 95%, identifying which subsystem failed—whether plasma source degradation, chamber contamination, or recipe drift—requires correlating dozens of variables.
Automated workflows parse this telemetry in real time, flagging anomalies before they cascade into tool crashes. By the time a technician receives dispatch, the platform has already isolated the likely failure mode, identified the degraded chamber component, and staged replacement parts—turning a 3-hour diagnostic hunt into a 20-minute validation check.
When multiple tools fail simultaneously—common during contamination events or recipe changes—the platform prioritizes dispatch based on production impact, tool criticality, and parts availability. It auto-generates triage recommendations, allocates technicians to highest-value interventions first, and pre-stages parts for sequential repairs to minimize total fab downtime.
The platform requires read access to tool sensor logs, alarm histories, and PM completion records. Most semiconductor OEMs provide this data via SECS/GEM interfaces or equipment data APIs. No modifications to tool controllers are needed—the system ingests existing telemetry streams and correlates them with service history.
Yes. The platform presents recommendations as validated starting points, not rigid mandates. Technicians can flag incorrect parts predictions, add manual observations, or deviate from suggested procedures. The system logs these overrides to refine future predictions and learns which tool-specific failure patterns require human judgment.
The mobile interface supports voice capture via fab-approved headsets or tablet microphones. Technicians dictate observations, part numbers, and actions taken without removing gloves or leaving the tool. The platform transcribes speech, auto-fills FSM fields, and attaches photos of replaced components—maintaining clean room protocols while eliminating manual data entry.
Technicians flag incorrect predictions via the mobile app. The platform logs the actual parts used, correlates telemetry with real-world outcomes, and updates prediction models. Over time, prediction accuracy improves from baseline 75% to 92%+ as the system learns tool-specific wear patterns and failure modes unique to each fab's operating conditions.

How AI bridges the knowledge gap as experienced technicians retire.

Generative AI solutions for preserving institutional knowledge.

AI-powered parts prediction for higher FTFR.
See how Bruviti transforms manual field service processes into automated execution plans.
Schedule Demo