When fab downtime costs $1M per hour, choosing the wrong field service AI approach risks months of development time or years of vendor lock-in.
Semiconductor OEMs face a choice: build custom field service AI in-house or adopt vendor platforms. Hybrid approaches combining pre-trained models with open APIs offer faster deployment without lock-in, letting technical teams extend systems using Python SDKs while avoiding costly ground-up development.
Building custom field service AI requires training models on equipment-specific failure patterns, integrating with FSM systems, and maintaining inference infrastructure. For semiconductor OEMs, this means collecting telemetry from lithography tools, etch chambers, and metrology equipment across multiple fabs before achieving reliable predictions.
Closed field service platforms trap technical teams in proprietary APIs and data formats. When you need to customize dispatch logic for EUV tool failures or integrate chamber-specific diagnostics, vendor limitations force workarounds or expensive professional services engagements.
Field service AI must connect to SAP for parts inventory, FSM systems for work orders, and equipment telemetry streams for failure prediction. Each integration requires custom connectors, data transformation pipelines, and ongoing maintenance as upstream systems evolve.
A hybrid approach combines pre-trained foundation models for common field service tasks with open APIs for semiconductor-specific customization. Bruviti's platform provides technician-facing AI trained on aftermarket service patterns while exposing Python SDKs for extending models with your equipment telemetry, historical failure data, and tribal knowledge.
This architecture eliminates the need to build predictive maintenance infrastructure from scratch while preserving technical flexibility. Your team controls deployment environments, trains custom classifiers for chamber-specific fault codes, and owns all training data. The platform handles model serving, version management, and inference optimization, letting your engineers focus on domain-specific logic rather than ML operations.

Predicts which chamber kits and consumables technicians need before dispatching to EUV or etch tool failures, reducing truck rolls for semiconductor equipment service.

Correlates process tool symptoms with historical failure patterns and captured tribal knowledge to identify root causes in lithography or deposition equipment faster.
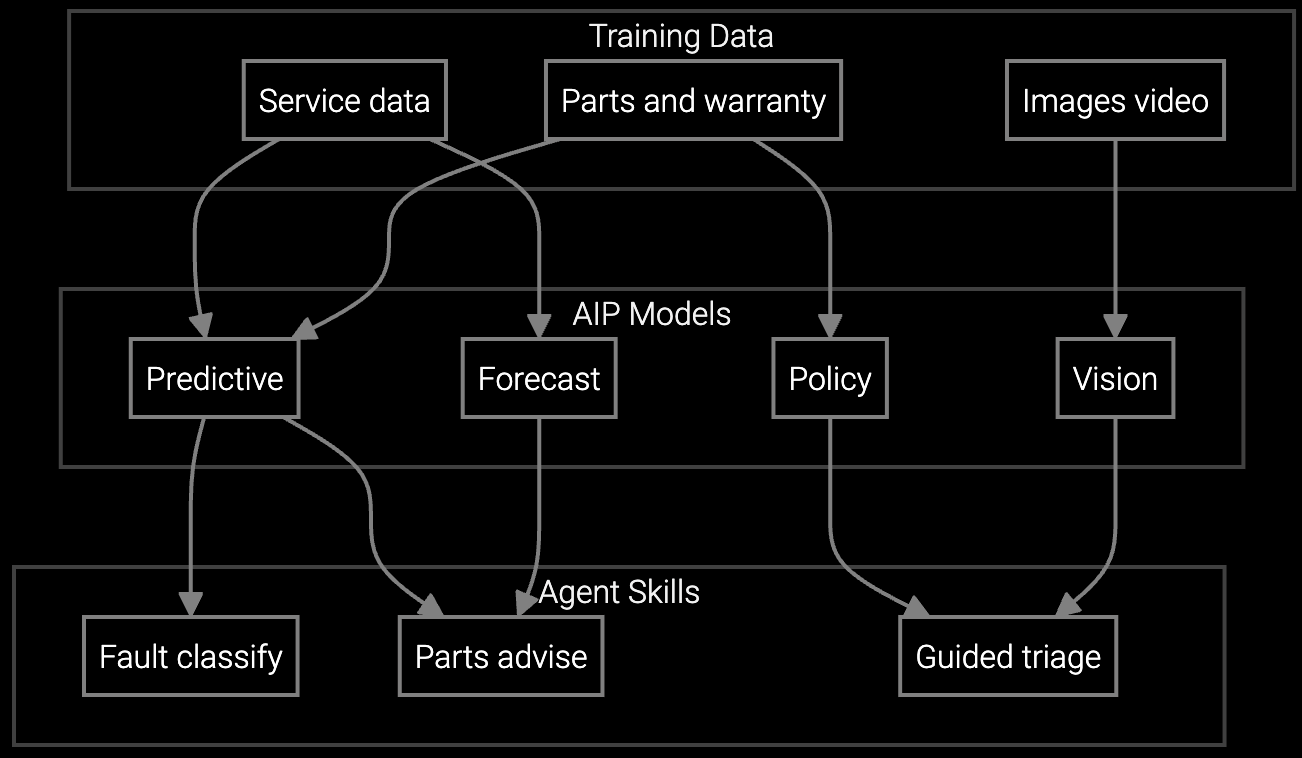
Mobile copilot provides real-time guidance on chamber cleaning procedures, recipe verification, and diagnostic steps specific to semiconductor fab equipment.
Semiconductor OEMs should start with high-value, high-complexity tools where technician expertise loss creates the most risk. EUV lithography systems and atomic layer deposition tools represent ideal pilots because failure patterns are complex, downtime costs are extreme, and tribal knowledge is concentrated in a small number of senior technicians.
Begin by integrating equipment telemetry streams from tool sensors with historical work order data from your FSM system. Use pre-trained models for initial parts prediction and root cause analysis, then extend them with chamber-specific fault codes and process recipe correlations using Python SDKs. This approach delivers value in weeks while building technical capability for broader rollout across metrology, etch, and packaging equipment lines.
Hybrid approaches using pre-trained models with open APIs typically reach production in 8-12 weeks for initial use cases like parts prediction. Building from scratch requires 18-24 months to collect training data, develop models, and build inference infrastructure. The hybrid approach front-loads value delivery while preserving flexibility to customize for semiconductor-specific requirements.
API-first platforms expose Python SDKs for extending pre-trained models with your equipment-specific logic. You can add custom classifiers for chamber fault codes, integrate proprietary telemetry streams, and implement fab-specific dispatch rules without modifying vendor code. Training data and custom models remain under your control, enabling migration to alternative platforms if needed.
Lithography tools, especially EUV systems, offer the highest ROI due to extreme downtime costs and diagnostic complexity. Etch and deposition chambers follow closely because consumable parts prediction directly improves first-time fix rates. Metrology equipment represents a third tier where AI assists technicians but lower downtime costs may justify later rollout priority.
Yes. Hybrid architectures support on-premises inference while accessing pre-trained models via API. Your equipment telemetry and service history never leave your network. You can fine-tune models locally using your data, then deploy them within your security perimeter. This preserves intellectual property while leveraging foundation models trained on broader service patterns.
Initial integrations include FSM systems for work order data, ERP for parts inventory, and equipment telemetry streams via SECS/GEM or OPC-UA protocols. API-first platforms provide pre-built connectors for common systems like SAP and ServiceNow, plus RESTful APIs for custom integrations. Most pilots complete integration work in 3-4 weeks using existing IT resources.

How AI bridges the knowledge gap as experienced technicians retire.

Generative AI solutions for preserving institutional knowledge.

AI-powered parts prediction for higher FTFR.
Explore Bruviti's hybrid architecture and developer tools for semiconductor equipment service.
Talk to Our Team